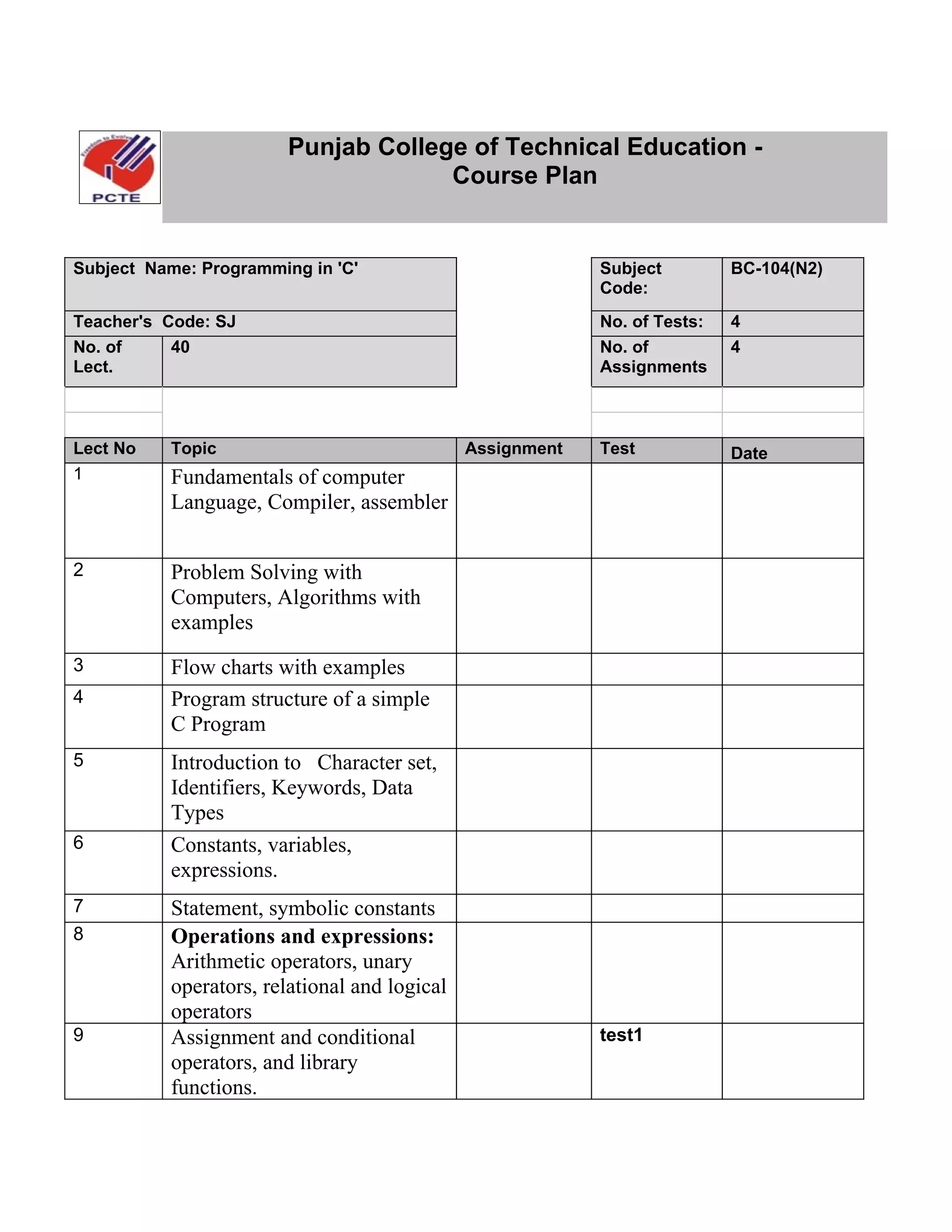
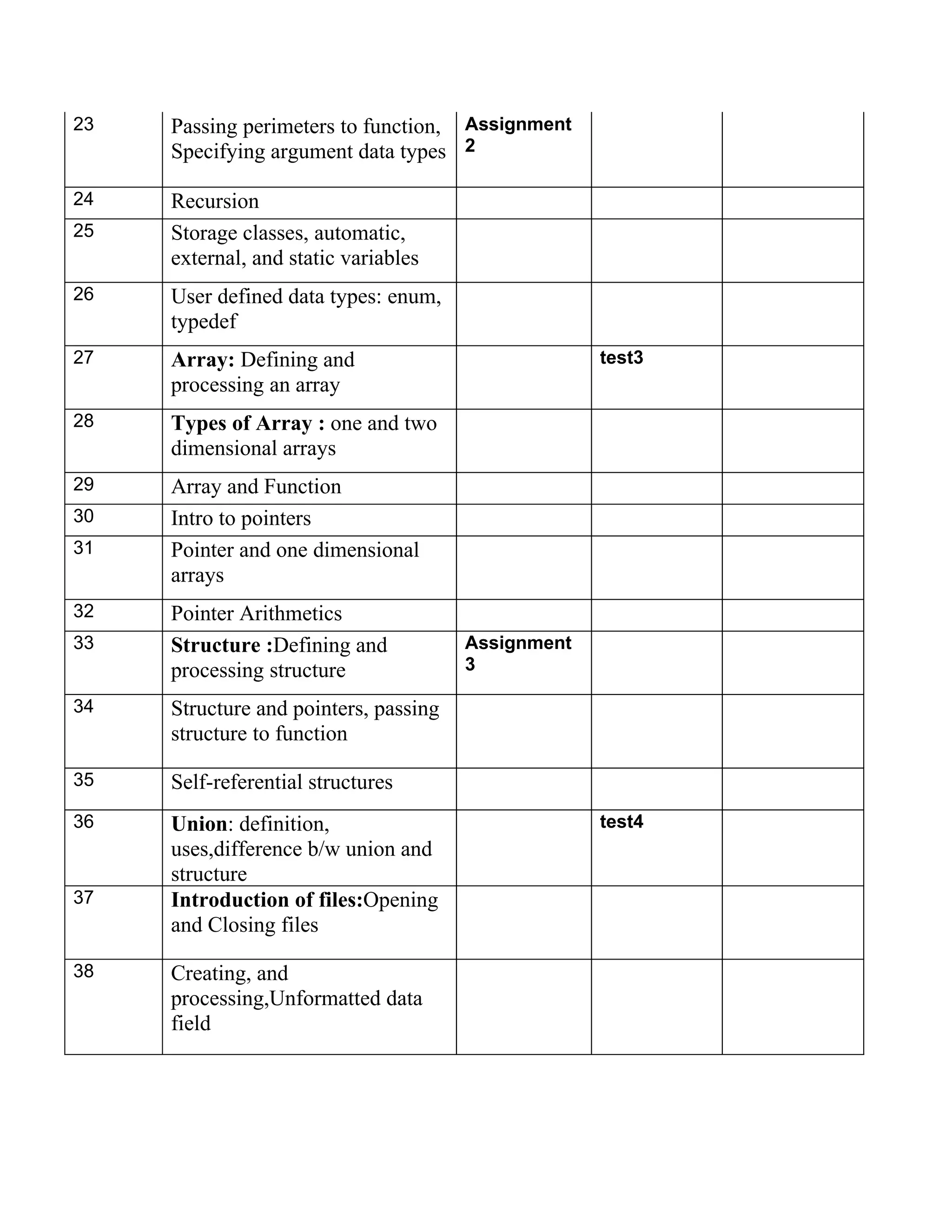
The document outlines the course plan for Programming in 'C' taught by Sandeepjit Kaur, including topics to be covered such as fundamentals, operators, input/output, control statements, functions, arrays, structures, unions, and files. It lists assignments, tests, and references to be used. The course will cover 40 lectures over the topics listed and include 4 assignments and 4 tests to assess student learning.